Lethality in the C. elegans infection model of P. aeruginosa ST17


Int. J. Mol. Sci., Volume 24, Issue 20 (October-2 2023) – 465 articles

Epidemiology, Biology, and Impact of Clonal Pseudomonas aeruginosa
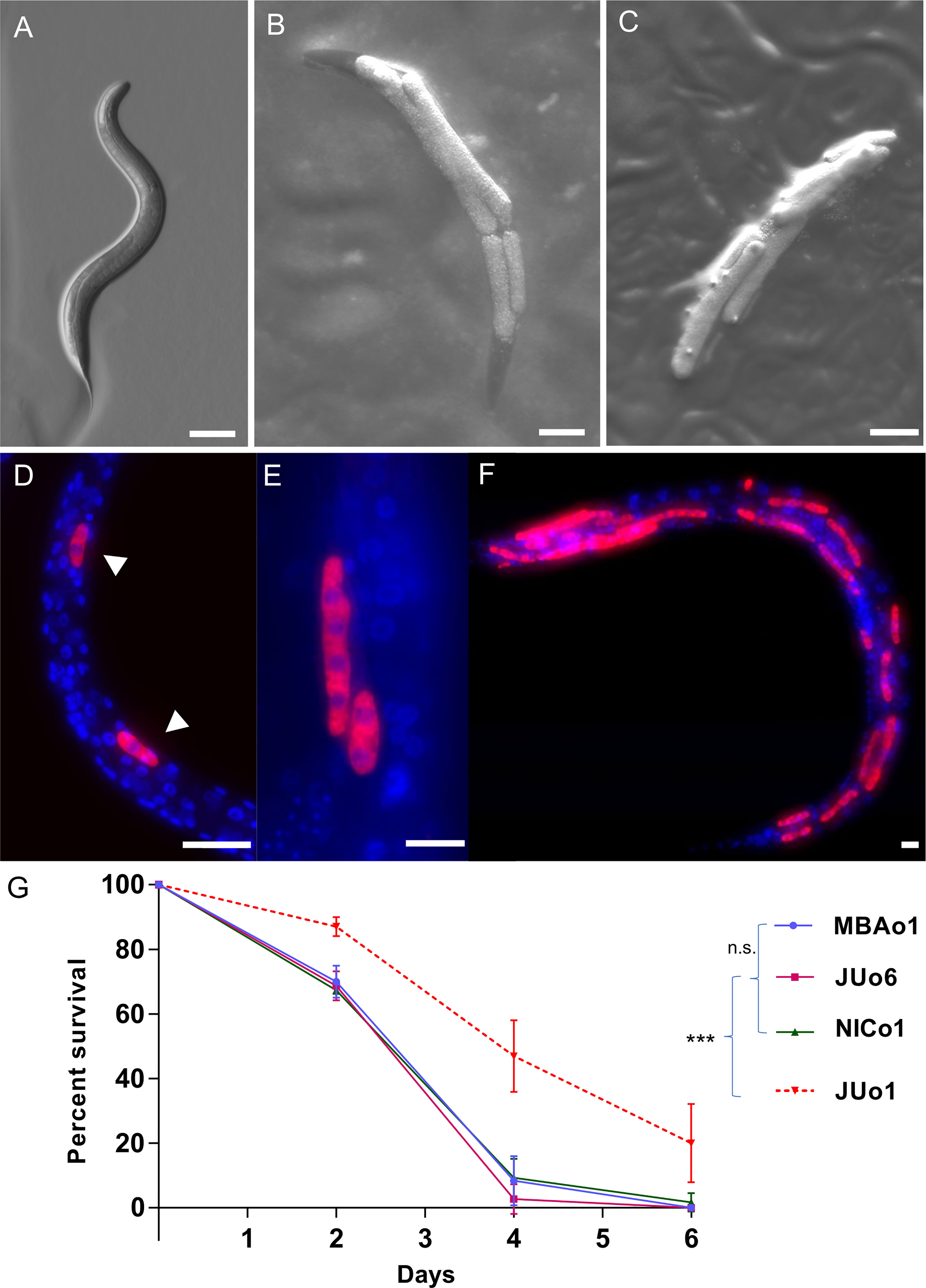
Frontiers Infection of C. elegans by Haptoglossa Species Reveals

Nosocomial outbreak linked to a flexible gastrointestinal endoscope contaminated with an amikacin-resistant ST17 clone of Pseudomonas aeruginosa

Felipe Fernández-Cuenca's research works Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Sevilla and other places

Autophagy protects C. elegans against necrosis during Pseudomonas
High-throughput phenotyping of infection by diverse microsporidia

Pseudomonas donghuensis HYS virulence towards Caenorhabditis

Lethality in the C. elegans infection model of P. aeruginosa ST17

PDF) Pathogenic characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa

Ubiquitin-related processes and innate immunity in C. elegans

Gabriel CABOT, PhD Student, Biology, Antibiotic Resistance and Pathogenicity of Bacterial Infections Group

Survival upon Staphylococcus aureus mediated wound infection in

Pseudomonas donghuensis HYS virulence towards Caenorhabditis







