Management of Onychomycosis and Co-Existing Tinea Pedis - JDDonline - Journal of Drugs in Dermatology

AbstractOnychomycosis is a common infection of the nail that often co-exists with tinea pedis. Surveys have suggested the diseases co-exist in at least one third of patients, although actual numbers may be a lot higher due to significant under-reporting. The importance of evaluating and treating both diseases is being increasingly recognized, however, data on improved outcomes, and the potential to minimize re-infection are limited. We review a recent post hoc analysis of two large studies treating mild to moderate onychomycosis with efinaconazole topical solution, 10%, demonstrating that complete cure rates of onychomycosis are significantly improved when any co-existing tinea pedis is also treated.J Drugs Dermatol. 2015;14(5):492-494. Onychomycosis, Proximal Subungual, Distal Subungual, Tinea Unguium, Tinea PedisOnychomycosis, Proximal Subungual, Distal Subungual, Tinea Unguium, Tinea Pedis

British Association of Dermatologists' guidelines for the
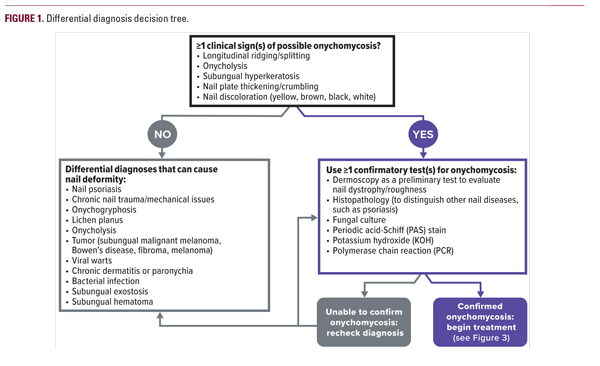
Therapeutic Recommendations for the Treatment of Toenail

PDF) Detection and relevance of naftifine hydrochloride in the
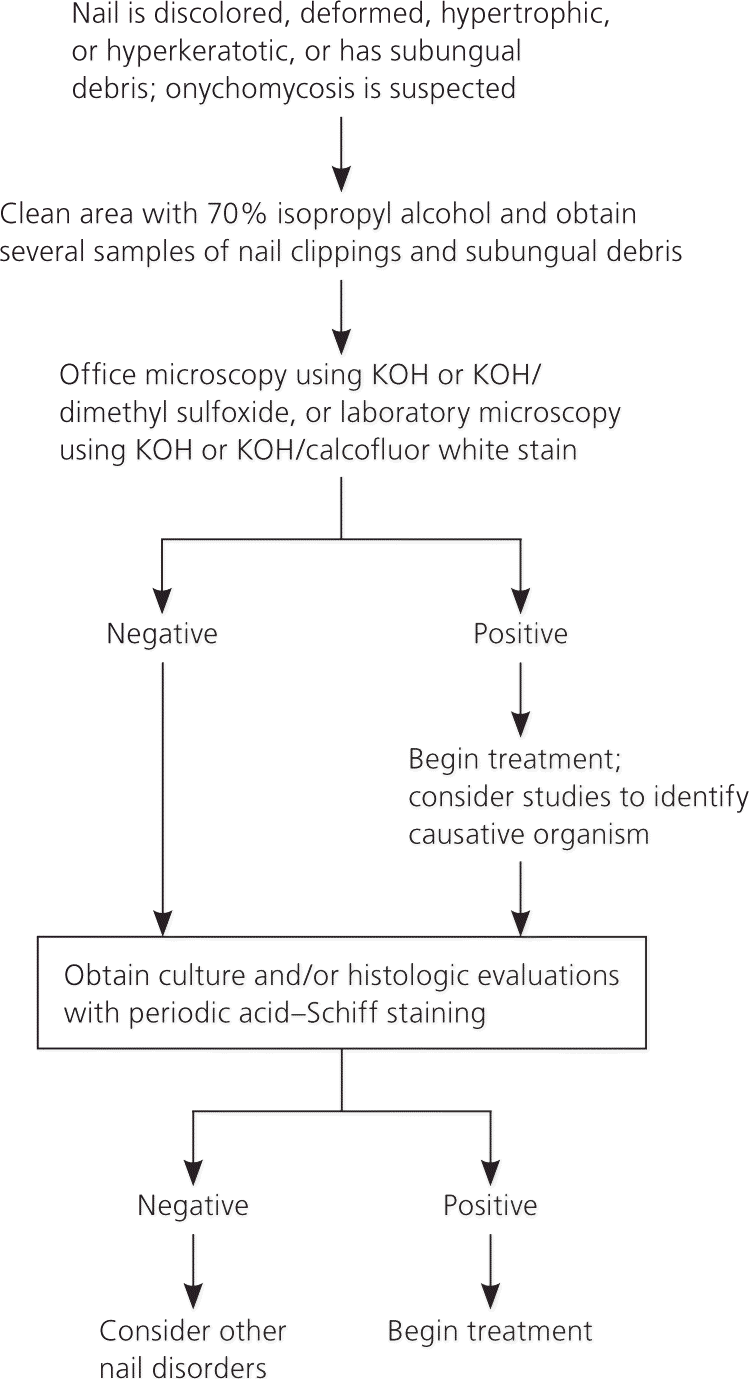
Onychomycosis: Current Trends in Diagnosis and Treatment
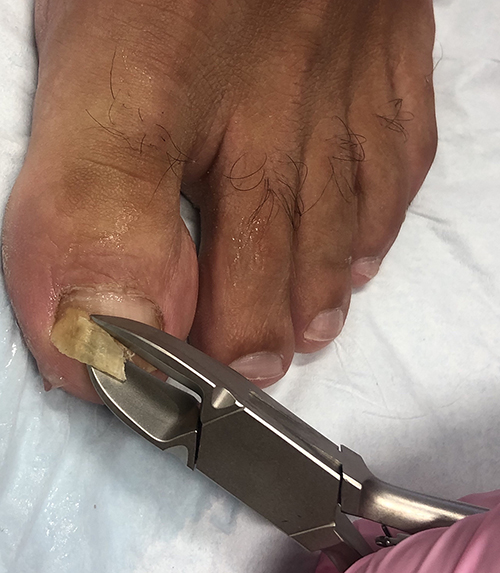
Perspectives on the diagnosis & management of onychomycosis
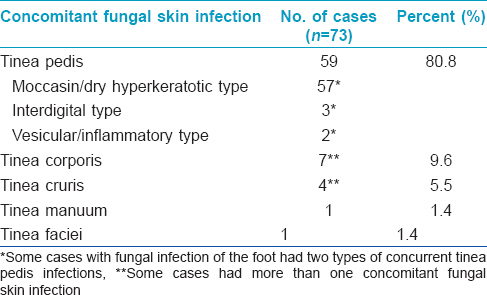
Onychomycosis: A study of self-recognition by patients and quality

Treatment and management strategies of onychomycosis - ScienceDirect

Assessment of Dermatophytosis Treatment Studies: Interpreting the

Onychomycosis Treatment Prescribed at Only Twenty Percent of

Onychomycosis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment in a
Onychomycosis: Rapid Evidence Review

Clinical Insights About Onychomycosis and Its Treatment: A






