The compressibility factor Z a low-pressure range of all gases except hydrogen is:Z=(1+ displaystylefrac{a}{V_{m}RT})Z =(1-displaystylefrac{a}{V_{m}RT})Z=(1+displaystylefrac{Pb}{RT})Z = ( 1 - displaystylefrac{Pb}{RT})

Click here:point_up_2:to get an answer to your question :writing_hand:the compressibility factor z at a lowpressure range of all gases except hydrogen is
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ✍️ The compressibility factor Z a low-pressure range of all gases except hydrogen is-Z-1- displaystylefrac-a-V-m-RT-Z-1-displaystylefrac-a-V-m-RT-Z-1-displaystylefrac-Pb-RT-Z - - 1 - displaystylefrac-Pb-RT-
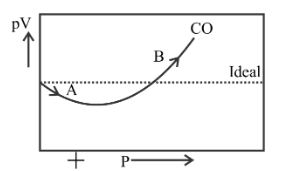
The van der Waals equation for real gases is -P-aVm2-Vm-x2212-b-RT

Compressibility factor - Wikipedia

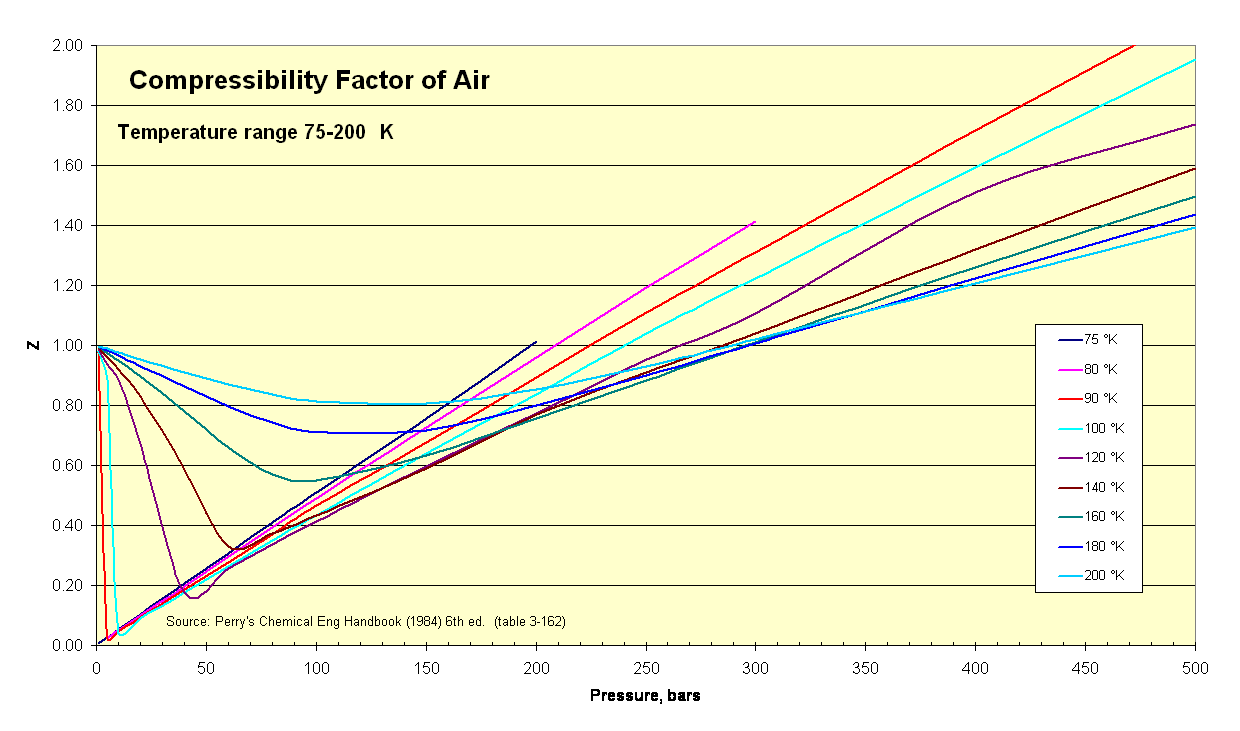
As the pressure approaching zero i.e., very low pressure, the curves plotted between compressibility factor Z and P n mole of gases have the following characteristics.I. The intercept on the y-axis leads

The compressiblity factor Z for 1 mole of a real gas at low pressure can be written as

If `Z` is a compressibility factor, van der Waals' equation at low pressure can be written as

3.2 Real gas and compressibility factor – Introduction to Engineering Thermodynamics

Gas Compressibility - an overview

Compressibility Factor - an overview

What is the compressibility factor (Z) for 0.02 mole of a van der Waals's gas at pressure of 0

Numerical simulation of single-phase two-component non-Darcy flow in naturally fractured reservoirs for enhanced gas recovery and carbon dioxide storage
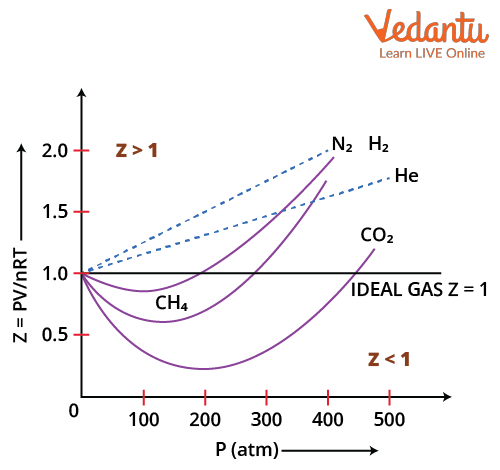
Compressibility Factor Z Important Concepts and Tips for JEE Main